Trunk Port or trunking is a term most frequently used in IT and telecommunications. For example, the trunk of a tree carries water and essential nutrients to all the branches and leaves of a tree. Trunk works exactly in the same way. In my article, I will explain to you why this term plays a vital role in the IT and telecom industries. The Trunk Port and an access port are the most confusing terms in the world of cisco world. I have also shared the comparison chart of the trunk port and access port for you. So, let us jump into the actual information now! Here you get the address lookup.
What Is Trunk Port?
A trunk port carries the signal traffic of all the VLANs which access the specific switch. The port trunk marks the tag to the frame as 802.1Q tag or the common technique Inter-Switch Link (ISL)tag. Thus, every single frame can be reached to the VLAN. A trunk port is configured to send packets from more than one VLAN without having the traffic. The trunk port accesses all the VLANs by default. Hence, a trunk port will stop the traffic from particular VLANs from passing over the trunk.
click here – How to Make Your House Look Good: The Ultimate Guide?
Uses Of Trunk Port
We have now learned about the trunk and its mechanism. Let us now see what are the uses of a trunk port.
- A trunk port transmits data from multiple VLANs.
- If you have more than one switch in the organization, you can just implement a single link to replace it by using any cables.
- The latency is lower in the trunk port.
- A trunk port will allow you to send all the signals in each switch by using a single trunk link.
- The bandwidth of the trunk port is very high.
Trunking Mechanism
The primary function of the trunking mechanism is to carry traffic between switches and maintain the VLAN information. Here the task is of the two different methods.
- Native VLAN: When the traffic sends between the devices without adding anything is called Native VLAN. The default setting in the native VLAN is set to VLAN 1. This setting allows the traffic to send between all the ports of more than one switch without any additional configuration.
- Tagging Mechanism: It adds the tag to the frame header in the Ethernet interface. There are two types of trunking mechanisms- symmetrical trunking and asymmetrical trunking. Let us see what actually these terms are.
- Symmetrical Trunking: This trunking mechanism will send the packets to any ports. Here, the transmission rate is very high.
- Asymmetrical Trunking: This type of trunking mechanism will send the packets using only one port in the switch.
VLAN Trunk Port
It is very important to understand why networks have VLANs. You must be wondering what is trunk port VLAN? Don’t worry I have a solution for this. Basically, VLANs are used to migrate some difficulties with switched networks that have replaced hubs. Switched networks have a flat topology that can create some congestion problems. Here, VLANs offers a solution for you. A VLAN provides connectivity for subnets on a network. With the help of VLAN, it is possible to configure a single switched network without doing physical network changes. Network switches support VLAN and create a Layer 2 subnet implementation.
Importance Of Trunking To Configure With VLAN
It is necessary to ensure that the signals are reaching the destination address when multiple VLANs are connected. It gets more complicated when more than one VLAN is connected to a single port. The system needs to understand and route the signals. In that case, VLAN trunking is used for marking the tag in the header. Trunking can be possible when you are working for multiple vendors. The Cisco VLAN Trunking Protocol is used here. This will automatically distribute the packets between the switches and will reduce your configuration time.
The trunking can be sometimes used for maintenance activity.
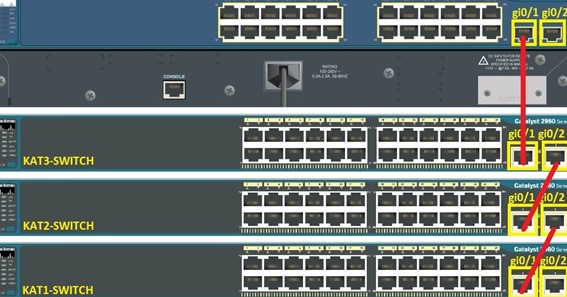
In order to use VTP, you must ensure that at least one trunk port is configured on the switch. And this trunk port is further connected to the trunk port of a second switch. Continue reading if you want to learn how to configure a trunk port on the cisco 2960 switch.
Step 1
Enable the configuration mode on the terminal.
>enable
#configure terminal
Step 2
Go to the interface on which you want to enable trunk mode.
(config) #interface (port)
Step 3
Click on the RUN command.
(config-if) #switchport mode trunk
(config-if) #end
Step 4
Show interfaces interface-id switchport
Copy running-config startup-config
Trunk Port Vs Access Port
Let us now discuss what exactly Trunk Port vs Access Port means in the world of VLAN. So here, I will give you the basic knowledge of these two most confusing terms in the cisco world. Each port on the Cisco switch can be configured as an access or a trunk port. Here is the description of these two port types in short.
In simple words, the trunk in VLAN carries streams of signals to the correct destinations or locations. It simultaneously carries many signals which creates more efficient network access between the two nodes.
Now have a look at the Access port. An access port is used to connect a guest Virtual machine that is VLAN. VLAN is a type of connection on a switch. The access port is generally configured on switch ports that are connected to devices with a normal network card. The frames that arrive on access ports are assumed to be part of the access VLAN.
click here – What Is EBGP (External Border Gateway)?
Trunk Port Vs Access Port DIfference
So now let us study the difference between Trunk Port and Access Port in detail.
- Generally, the trunk port supports only the tagged frames. Whereas the access port sends and receives untagged frames.
- The trunk port allows you to switch multiple VLANs. In the access port, all the frames are in the same VLAN.
- A trunk port basically is used to connect between the different switches. An access point is used to connect laptops, printers, and some other devices.
- In the trunk port, you cannot extend the data from one switch to another switch, i.e., access ports via a trunk port. You can only extend it via the access port of the switch.
- The trunk port has more than one VLAN set up on the interface. While an access port is capable of having only one VLAN set up on the interface.
- Usually, the trunk port offers higher bandwidth and lower latency when compared to the access ports.
- The trunk port does not support the voice VLAN feature. While the voice VLAN feature is supported on the access port.
- A trunk port will add a dot1q or ISL (inter-switch link) tag directly to the frames. Whereas the access port only passes traffic from a set VLAN which doesn’t modify the frame with a VLAN Tag.
Trunk Port Vs Access Port Comparison
Now let us have a look at the table of comparison between the trunk port and an access port to understand it better.
[table id=4 /]
Trunk Port Vs Tagged Port
Let us now compare the two terms trunk port and tagged port.
You know that it allows you to send all the signals for each switch or router across a single trunk line. Hence, this port must use tagging in order to allow signals to get to the correct endpoint.
A port is considered a tagged port when the interface is expecting frames containing VLAN tags. Usually, cisco switches use the term trunk to refer to a tagged port.
Trunk Port And OSI Layer 2
Usually, the trunking of the involved VLANs takes place in layer 2 of the OSI model. It designates seven different layers for network transmissions. Layer 2 is also well-known as the data link layer. It is typically used for MAC broadcasting and signaling between nodes of an internal network. Layer 3 is mostly used for segmented IP routing.
IP Trunking
An IP trunking is a transmission technique for the large-scale use of Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP). This means that the service provider utilizes an IP trunking to both send and receive switches for each call. It involves sending voices over the internet as data, rather than as electrical signals. A typical trunking configuration is the Privacy Branch Exchange (PBX). This PBX system can address and route the packets to the receiving endpoint. This IP transmission process occurs over the caller’s unique IP address. Sometimes, IP trunking may happen on the backend, but VoIP is still relevant for many MSPs (Managed service providers).
Read Also: Reasons Why It Is A Good Idea To Hire An Online Tutor
FAQ
What Is A Trunk port?
A trunk port carries the signal traffic of all the VLANs which access the specific switch. This port marks the tag to the frame as 802.1Q tag or the common technique Inter-Switch Link (ISL)tags.
What Is The Difference Between Access And Trunk Port?
The main difference between access and trunk port is that trunk port supports only the tagged frames. While the access ports send and receive untagged frames.
What Is The Purpose Of Trunking?
The central purpose of trunking is to carry traffic between switches and maintain the VLAN information. It helps to carry traffic from several VLANs over a point-to-point link between two devices that understand the protocol.
What Is VLAN Trunking Used For?
VLAN trunking is used for extending a VLAN across the network. It enables the movement of traffic to different parts of the network configured as a VLAN.
How Many Trunk Ports Per Switch?
There are two switches on a trunk port. Thus, you can carry more than one VLAN traffic from one switch to another switch.
Do Trunk Ports Pass All VLANs?
By default, a trunk port sends traffic to and receives traffic from all VLANs. All VLAN IDs, 1 to 4094, are allowed on each trunk. However, you can remove VLANs from the allowed list, preventing traffic from those VLANs from passing over the trunk.
When Would You Use A Trunk Port?
The purpose of a tagged or “trunked” port is to pass traffic for multiple VLAN’s, whereas an untagged or “access” port accepts traffic for only a single VLAN. Generally speaking, trunk ports will link switches, and access ports will link to end devices.
Why Is It Called A Trunk Port?
trunks that carry data from multiple local area networks or virtual local area networks (VLANs) across a single interconnect between network switches or routers, called a trunk port.
What Is Trunk Vs Uplink Port?
An uplink port would be used to pass traffic to another switch or router or network device. A trunk port would be used to pass VLAN traffic between two switches or other network devices.
Read Also: Top 5 Mistakes to Avoid When Installing Solar Systems
Conclusion
Many businesses and large organizations require a trunk port to handle multiple call lines. In my above article, I have explained the about it and its mechanism. This port can transmit data from multiple VLANs by default. I have also discussed the uses of the port. Here, trunking allows multiple calls to go through simultaneously. Basically, we can say trunk port is a link that carries many signals simultaneously.
To Know Some Great Stuff Do Visit fyndblog
To Know Some Great Stuff Do Visit fixznow
To Know Some Great Stuff Do Visit turnoffme
What is the purpose of a trunk port